“What happened? My heart is beating so strong and is anything going wrong? I can feel the pumping from my eyes and … my neck. Not gonna lie. My heart is tingling. I wanna throw up.”
Have you felt that way, and the shock that you might have a heart attack just kicked in? Dude, take a break, and you should have your heart checked; resting ECG, which you might be prescribed, is one of the effective tests to detect abnormalities.
An Overview of SVT and the Different Types of SVT
Supraventricular tachycardia, commonly known as SVT, is a form of arrhythmia. It occurs whenever a rapid or irregular heartbeat can impact the heart’s upper chambers.
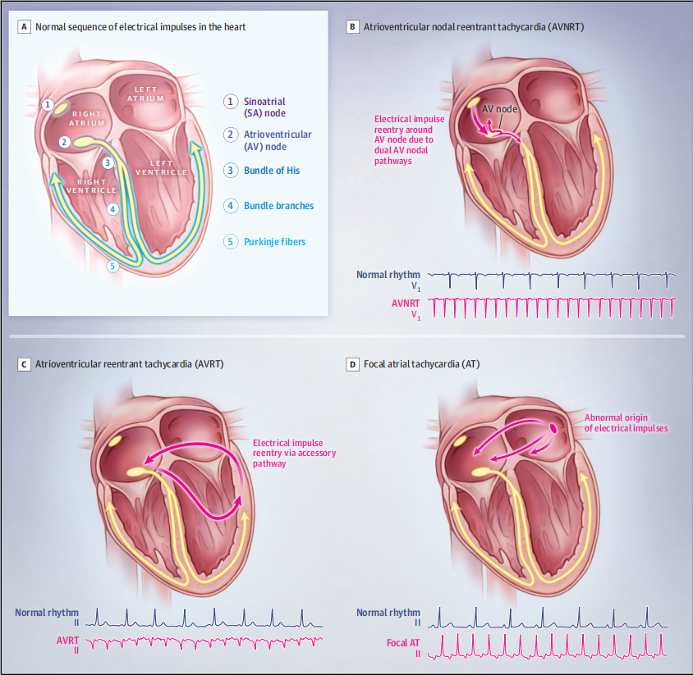
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common arrhythmia we frequently encounter in clinical practice. It typically presents as a narrow QRS complex tachycardia, though it may manifest as a wide QRS complex tachycardia when a bundle branch block is also present. SVT primarily includes atrial tachycardia (AT), atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), and atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT).
A normal heart beats between 59 and 99 times per minute. However, depending on the heart’s state during SVT, the rate may vary between 150 and 220 times per minute.
Types of SVT
Below are the types you need to know.
● Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
It is common, especially among young females. It occurs due to an additional pathway in the heart close to the AV node. It causes the electrical signal to loop instead of moving down to the heart’s lower chambers, triggering a sudden and rapid heartbeat.
● AV Reciprocating Tachycardia (AVRT)
It happens when an abnormal pathway links the lower and upper chambers of your heart. It leads to causing the signal to move in a big loop.
● Atrial Tachycardia
It occurs due to a short circuit in the left or right atrium of your heart initiates a wrong electrical signal. It typically affects people with heart disease.
Common Symptoms of SVT and Its Health Effects
SVT is a fast heart rate that originates above the heart’s ventricles. Some of the most common symptoms of this problem are:
- Palpitation
- A pounding feeling in your neck.
- Chest pain.
- Fainting or feeling like you might faint.
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
- Trouble breathing or shortness of breath.
- Feeling weak or extremely tired.
- Sweating.
The ECG Tracing of Typical ANVRT, O-AVRT, And A-AVRT
The resting ECG is an important medical test that helps measure the state of the heart. The resting ECG test determines the heart’s electrical activity when inactive, providing important information about the heart’s rate.
Mechanism of Resting ECG
In resting ECG, there is no need to perform any exercises, unlike the exercise ECG. Often, it is done to assess your heart status when you are not exerting yourself at all. It is very brief, and it is not at all invasive. It is just a very smooth process.
The resting ECG can help find certain heart problems.
It can show signs of previous heart attacks. It also enables the identification of SVT to understand problems with heartbeat rhythms and heart muscle thickening. It usually takes 10 minutes to complete.
The ECG Tracing of Typical AVNRT, O-AVRT, and A-AVRT
AVNRT
In typical AVNRT, the backward P waves appear early. This means we either can’t see them because they are hidden in the QRS wave, or we can see them only a little. They may show up as a small bump at the end of the QRS complex.
O-AVRT
When looking at an ECG for AVRT with orthodromic conduction, you might notice:
- Heart Rate usually ranges from 200 to 300 beats per minute.
- Backward P Waves are typically visible and have a long RP interval.
- The duration of the QRS is usually less than 120 milliseconds unless there is a pre-existing bundle branch block or if the heart rate causes abnormal conduction.
- QRS Alternans refers to a change in the height of the QRS waves. It happens with each heartbeat, as seen in both AVNT and AVRT. Unlike electrical alternans, the overall height of the QRS remains normal.
A-AVRT
- Heart Rate typically ranges from 200 to 300 beats per minute.
- The QRS complexes appear wide because the ventricles are not depolarising normally through the usual pathway.
EDAN ECG SE-1200/SE-1201 is a Recommended Solution to Trace SVT
EDAN ECG SE-1200/SE-1201 has been proven to be the catalyst of clinical efficiency.
Portable Design for Mobility
These ECG machines incorporate a highly portable concept, making them ideal for use in a variety of settings, including patient transport, ward rounds, and emergency care. Physicians can easily carry the devices.
Innovative, Easy-to-Clean Glass Panel
Both models feature a revolutionary all-glass front panel designed for easy cleaning and disinfection. This not only ensures better hygiene in clinical environments but also offers long-term durability.
High-Definition Capacitive Touch Screen
The SE-1200 and SE-1201 are equipped with high-definition capacitive touch screens, along with ultra-sensitive light-sensing buttons.
Comprehensive ECG Collection
Supporting 12-lead ECG collection, these devices provide complete cardiac data for accurate diagnosis. They also feature a unique 9-lead pediatric collection mode tailored specifically for children.
With a pediatric-specific algorithm, these models can distinguish between different age groups, ensuring reliable ECG recordings and accurate diagnosis for younger patients.
Advanced Pacemaker Detection
With an impressive 80,000 Hz pacemaker sampling rate, the SE-1200 and SE-1201 excel in detecting even the slightest abnormalities in heart rhythm, capturing critical heart signals that can be missed by standard machines.

Conclusion
Understanding SVT and its types is important to identify and manage these conditions in a timely manner. This guide is certainly helpful for tracing these conditions on Resting ECG.
For more phenomenal medical devices, you can visit EDAN.