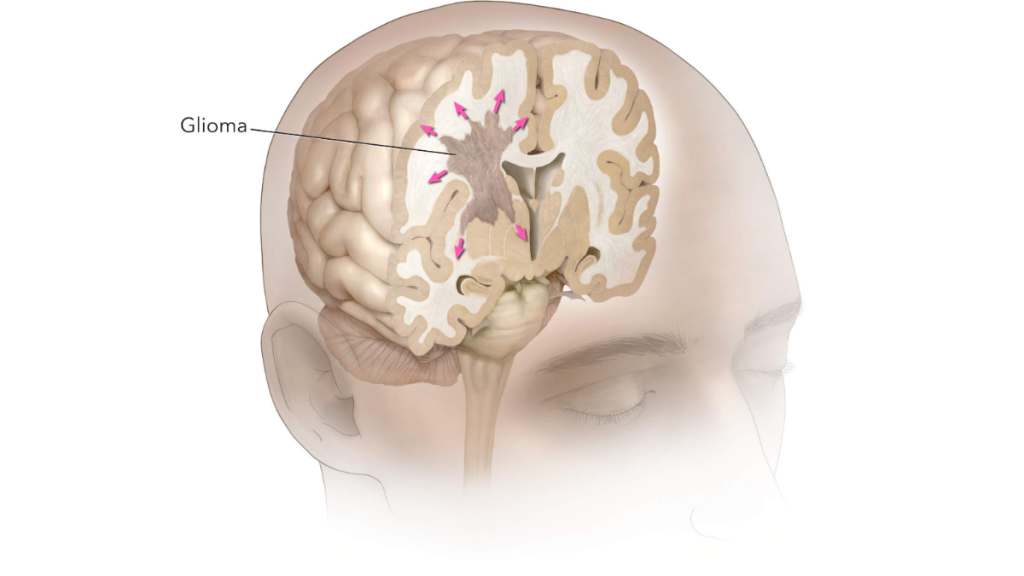
A glioma is an insidious type of cancerous tumor that originate in the brain or spinal cord. It’s important to understand what gliomas are, why they occur, and the treatment options available. Knowing more about gliomas can help you make informed decisions when it comes to your medical care or the treatment of someone close to you.
Gliomas are classified according to the type of cells affected and how aggressive they are. The four primary types of gliomas include astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, ependymoma, and mixed glioma.
Astrocytomas
Approximately 50% of all brain tumors are astrocytomas, making them the most prevalent type of glioma. Astrocytomas are derived from star-shaped cells called astrocytes. These cells provide tissue structure, help transmit signals from one nerve cell to another, and regulate chemicals within the brain. Astrocytomas can range from low-grade tumors that grow slowly over time to high-grade tumors that grow more quickly and require more aggressive treatment.
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas arise from oligodendrocytes, which are cells that form a fatty substance called myelin around nerve fibers. Oligodendrogliomas tend to be slow-growing tumors and often respond well to treatment but may recur after several years.
Ependymoma
Ependymomas are tumors of the ependymal cells, which are thin membrane-like tissues that line the ventricles (fluid-filled cavities inside the brain and spinal cord). They can be low-grade or high-grade, depending on the tumor’s aggressiveness.
Mixed Gliomas
Mixed gliomas are tumors that contain more than one type of cell, such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. They are usually high-grade tumors, often requiring more aggressive treatment.
Diagnosis & Treatment Options of Gliomas
Gliomas are diagnosed using imaging techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans. Once a glioma is diagnosed, the patient and their doctor will discuss treatment options. Treatment options will depend on the size, location, type of gliomas, and aggressiveness of the tumor as well as overall health history and lifestyle factors.
Common glioma treatments include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery, proton therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. The specific treatment plan will be determined by your doctor based on these factors. In some cases, watchful waiting may also be recommended if the tumor poses no immediate threat at this time.
Complications & Prognosis
Gliomas can cause complications such as seizures, vision changes, memory problems or speech difficulties, depending on their location in the brain or spine. Treatment options can also have potential side effects, including fatigue and nausea for chemotherapy or skin irritation for radiation therapy. Depending on the tumor’s size and position as well as other factors like age and overall health status, the prognosis can range from very good to very poor.
Conclusion
Gliomas come in many shapes and sizes, so it’s important for doctors to properly diagnose each individual case before recommending treatment options. With early detection through regular scans or MRI imaging tests, these tumors can be treated through surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of treatments depending on the individual case. Knowing which type of glioma you have will empower you to make well-informed decisions regarding your treatment plan in collaboration with your healthcare team.