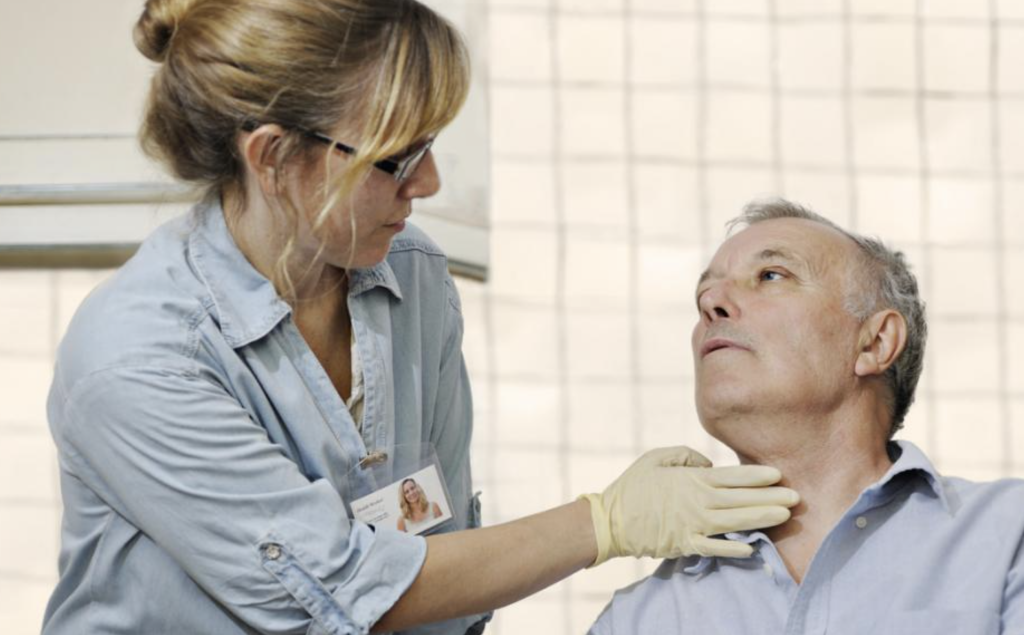
Dysphagia essentially means a swallowing difficulty. It involves more effort than normal for food to pass from the mouth down to the stomach. Normally caused by muscle or nerve problems, dysphagia is painful and common in seniors and babies.
Even though “dysphagia” is a medical term usually referenced as a sign or symptom, it is at times used when describing a condition. There are different causes of dysphagia. In the case where it occurs once or twice, the likelihood of a serious underlying problem is very slim. However, if it happens regularly, you will need to consult a doctor.
Since there are numerous reasons for the occurrence of dysphagia, treatment will depend on its underlying cause. This article serves to shed more light on dysphagia, you will hopefully be able to make more informed decisions after reading it.
What is Dysphagia?
Like earlier mentioned, dysphagia is a swallowing difficulty. It can happen in any phase of swallowing. These are:
- Oral
- Pharyngeal
- Esophageal
This condition is usually noted in survivors of stroke. It can affect the pharyngeal and/or oral swallowing phase. The person might choke or cough while trying to swallow food, liquids or even saliva.
Speech-language pathologists will often assess patients’ ability to swallow to ascertain aspiration risks (this is liquid or food entering the lungs). This may result in pneumonia or lung infection.
Causes of Dysphagia
The following are some of the possible causes of this condition:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis — this is a kind of progressive neuro-degeneration that is incurable. In the long run, the spine and brain nerves will start to lose function.
- Achalasia — this is when the lower esophageal muscle isn’t relaxed enough for food to enter the stomach.
- Stroke — this is when brain cells die as a result of insufficient oxygen caused by reduced blood flow. If the cells in charge of swallowing become affected, this could lead to dysphagia.
- Esophageal ring — this occurs when a small part of the esophagus reduces in size, which will then prevent the swallowing of solid foods.
- Multiple sclerosis — this occurs when the immune system attacks the nervous system, destroying myelin in the process.
- Parkinson’s disease — this is a degenerative neurological disorder which affects the motor skills.
- Radiation — a handful of patients that received radiotherapy of the head and neck area may encounter swallowing difficulties.
- Scleroderma — this is an autoimmune disease where there is tightening and hardening of the skin as well as connective tissues.
Rehabilitation that can help with Dysphagia
Rehabilitation has proven to be helpful to people. Speech-language pathologists will be able to teach exercises that will help to strengthen swallowing muscles. For safe swallowing, speech-language pathologists may recommend the following:
- Change your eating and drinking habits: The therapist will most likely advise that you take smaller bites while thoroughly chewing the food. You might have to add thickening powder like SimplyThick Easy Mix to your drinks if liquids are difficult for you to swallow.
- Sit upright while eating: So as to decrease the risks of choking, you will be shown the most ideal way to sit when you’re eating. You will also be taught how to tilt your head so that swallowing can be easier. These techniques will decrease the risk of water and other liquids getting inside your airway.
- Clear your throat: You will likely be taught how to use a little cough to clear your throat if liquid or food gets stuck.