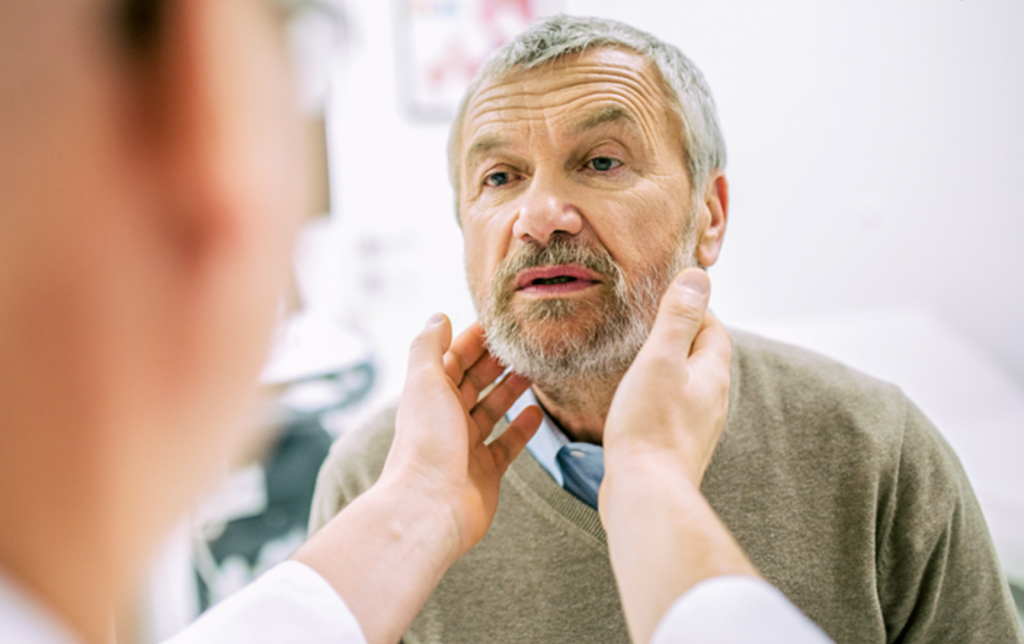
Thyroid nodules are unusual growths in the thyroid gland. Our thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system which controls the body temperature, cardiac functions and digestion. When there are thyroid nodules present, it can interfere with the thyroid hormone secretion which can ultimately hinder normal body functioning. If you suspect that there is an overgrowth in the thyroid gland, then it is best to have an ENT evaluation to rule out the presence of thyroid nodules.
The ENT Clinic is equipped with the latest technology and some of the best ENT doctors in Singapore who can help you out with a correct diagnosis. This ENT practice has state of the art facilities and caters to both adult and paediatric ENT disorders. It is important to know the causes behind thyroid nodules.
What causes thyroid nodules?
There could be many reasons to develop thyroid nodules. Some of these are:
Thyroid Adenoma:
An overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue can occur which is referred to as a thyroid adenoma. The exact reason why it happens is unknown and it is not cancerous. However, it can be bothersome to an individual and it can even lead to hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid Cyst:
A degenerating thyroid adenoma can result in fluid filled cysts or cavities. Cysts are generally non-cancerous but may rarely have cancer components. These cysts have solid components which are mixed with fluid in thyroid cysts.
Hashimoto’s Disease:
Chronic inflammation in the thyroid gland is a disorder which can result in enlarged nodules. It is due to hypothyroidism.
Multinodular goitre:
A thyroid disorder can lead to a goitre. It can be due to iodine deficiency. Multiple nodules can be present in a multinodular goitre. Lack of iodine in diet can cause thyroid nodules to develop and it is therefore important to consume iodised salt.
Thyroid Cancer:
During a very rare instance a thyroid nodule may be due to a malignancy too and thus, it is important to have an ENT evaluation to rule out cancer. In addition, hard, painful and large nodules are a concern which you should seek ENT help for. Genetic predisposition is another factor which increases the risk of cancer.
What are the different types of thyroid nodules?
Colloid Nodules:
Benign overgrowths of the normal thyroid tissue. It is present within the thyroid gland and doesn’t spread beyond.
Thyroid cysts:
Fluid filled or partially fluid filled nodules.
Inflammatory nodules:
Long term chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland can lead to the development of nodules. These growths may or may not cause pain.
Goitre:
It can form multi-nodules which are benign.
Hyper functioning thyroid nodules:
These are autonomously thyroid producing nodules which can lead to hyperthyroidism. It can lead to hypertension and cardiac arrest.
How do I know if I have a thyroid nodule?
Not all thyroid nodules produce symptoms. However, if there are several nodules or nodules which are large, the following symptoms may be seen:
- Neck pain
- Trouble swallowing
- Hoarseness in voice
- Enlargement in the thyroid gland
If hyper functioning thyroid nodules are present one would experience weight loss, muscle weakness, difficulty sleeping, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, itchy skin and vision problems.
Thyroid nodules can at times be associated with hypothyroidism symptoms of hoarse voice, fatigue, weight gain, forgetfulness, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, depression and generalised swelling.
How are thyroid nodules diagnosed?
Your ENT doctor will take a medical history and perform a physical evaluation. In addition to confirm, the following tests may be done:
Thyroid hormone level test:
This will help to check the level of thyroid hormones in the blood and any abnormal levels would be evaluated further.
Ultrasound:
An ultrasound scan of the thyroid will help to find nodules
Thyroid Scan:
This helps to determine the likelihood of cancer by using a small radioactive iodine dose given orally. The ENT doctor will evaluate how much of the radioactive iodine has been absorbed by the nodules.
Fine needle biopsy:
A small amount of cells are aspirated by a fine needle from the thyroid nodule. It is then assessed in the laboratory to check for any malignancy.The ENT doctor may suggest the nodules to be removed by surgery if needed.
Who needs a needle biopsy for their thyroid biopsy?
The otolaryngologist will perform a needle biopsy on any thyroid nodule which is big enough to be felt. Thus, nodules which are larger than 1cm or about half an inch across are usually considered for biopsy. Also nodules with microcalcifications which are coarse and 2cm in diameter or larger which have mixed solid and cystic components are considered for a biopsy. Nodules with irregular margins and where the length is greater than the width should be biopsied.
In addition, thyroid nodules which cause symptoms are considered. Any swollen or abnormal lymph nodes in the neck should be done especially to rule out a thyroid cancer. Also thyroid nodules which have a certain characteristic under the ultrasound should be considered for biopsy too.
What is the role of gene expression classification in assessing thyroid nodules?
Commercial molecular testing such as the use of gene expression classifiers (GCE) is now being used at The ENT Clinic by Dr Jeeve Kanagalingam, Dr Chritopher Hobbs and Dr Annabelle Leong to evaluate cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. It is effective in ruling out the presence of a malignancy. This is a great step in avoiding unnecessary surgery when a fine needle aspiration biopsy is indeterminate when cytopathology is used.
There are a high number of cases where people receive diagnostically ambiguous results. This has often caused total or partial thyroidectomy even for benign nodules. Thus, such surgeries can be avoided with the use of gene expression classifiers. It is a comprehensive solution to manage patients throughout the diagnosis process of thyroid nodules. This latest technique can save patients many dollars and unnecessary surgical risk.
What are the treatment methods for thyroid nodules?
If an individual has a benign thyroid nodule, then your ENT doctor will wait watchfully with regular physical examinations and thyroid function tests to see if the thyroid nodule is growing or not. Thyroid hormone therapy will be recommended if the gland is not producing enough thyroid hormone. Surgery may also be needed if the nodule is large and it is interfering with breathing and swallowing. Alternatives to surgery include microwave and radiotherapy ablation. Both are safe procedures for benign thyroid nodules.
Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive procedure which is also performed at the ENT Clinic Singapore. Guided by ultrasound imaging, this percutaneous treatment uses radio frequency waves to heat up the thyroid nodules. This process causes the nodule to shrink.
Treating cancerous nodules are usually done using alcohol ablation where a small amount of alcohol is inserted into the nodule. This is done multiple times to destroy the nodule. In addition surgery may be performed to remove the cancerous nodules.